X-ray diffraction is used for a wide variety of material characterization studies. Primarily, the technique identifies crystalline species in a material. For example, the specific iron oxide compound can be determined on steel scale. In addition to compound identification, XRD can also be used to determine strain, preferred orientation, crystallographic structure, and grain size of crystalline materials. When x-ray diffraction is used in a glancing angle mode, crystalline structure as a function of depth can be obtained.
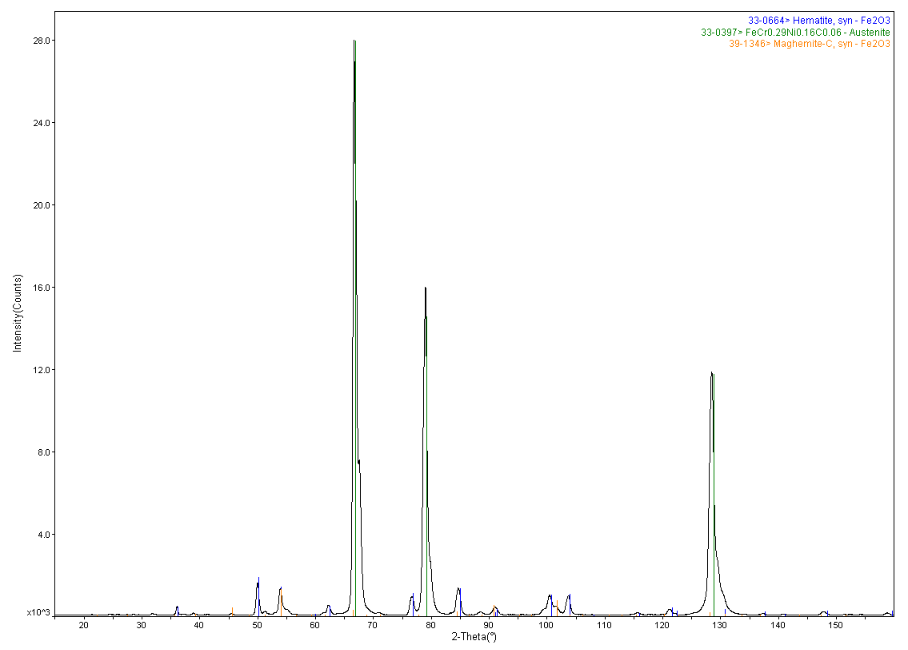
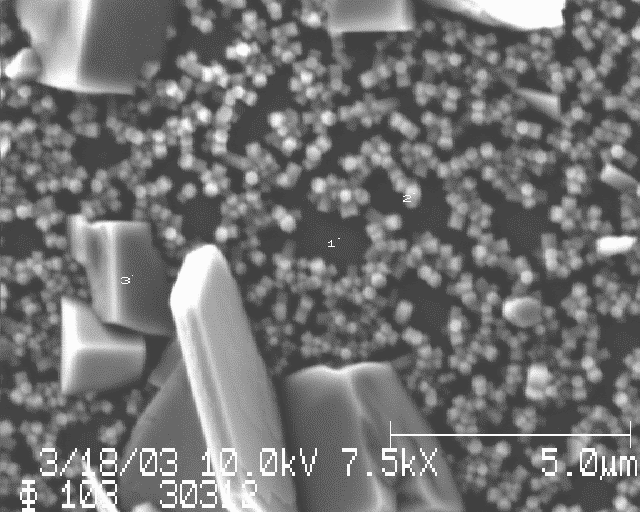
Oxide scale in stainless tubing
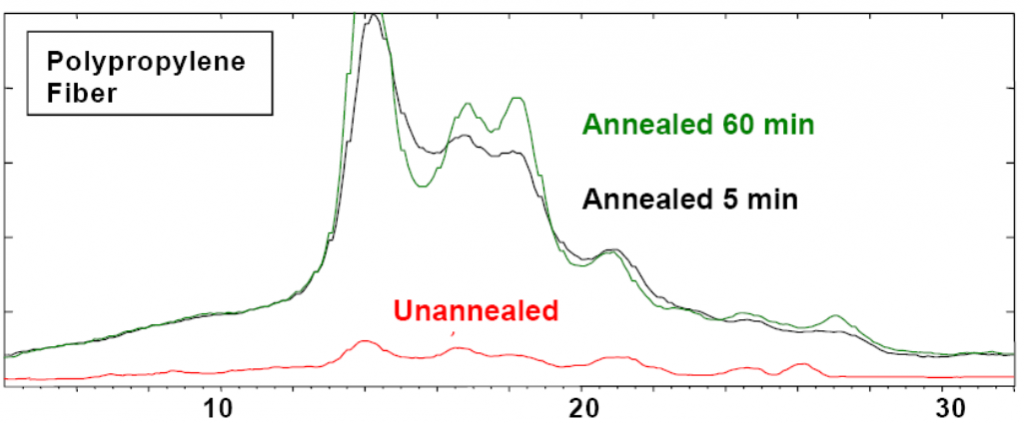
X-ray diffraction can also be used on organic materials, for example, to determine the degree of crystallinity of a polypropylene fiber as a function of annealing time. The differences were correlated to tensile strengths and elasticity data.